CKYC Registry
-
Customer Service Contact us Service request Locate a branch
Find all the help you need
Scan the QR, get our app, and find help on your fingertips

Help CenterSupport topics, Contact us, FAQs and more
-
Login
Are you ready for an upgrade?
Login to the new experience with best features and services
-
Login
Are you ready for an upgrade?
Login to the new experience with best features and services
- Accounts
-
Deposits
IDFC FIRST Bank Deposits
View all Deposits -
Loans
IDFC FIRST Bank Loans
View all Loans - Wealth & Insure
-
Payments
IDFC FIRST Bank Payments
View all Payments -
Cards
IDFC FIRST Bank Cards
View all Cards - Blogs
- Corporate Account
-
Cash Management Services
IDFC FIRST Bank Cash Management Services
View all Cash Management Services - Supply Chain Finance
-
Corporate Lending
IDFC FIRST Bank Lending
View all -
Treasury
IDFC FIRST Bank Treasury
See more details - NBFC Financing
Support topics, Contact us, FAQs and more
- IDFC FIRST Bank Accounts
-
Savings Account
-
Corporate Salary
Account -
Senior Citizens
Savings Account -
First Power
Account -
Current Account
-
NRI Savings
Account -
TASC Institutional
Account -
Savings Account
Interest Calculator
- IDFC FIRST Bank Deposits
-
Fixed Deposit
-
Recurring Deposit
-
NRI Fixed Deposit
-
Safe Deposit Locker
-
FD Calculator
-
RD Calculator
- IDFC FIRST Bank Loans
-
Personal Loan
-
Consumer Durable
Loan -
Home Loan
-
Business Loan
-
Professional Loan
-
Education Loan
-
New Car Loan
-
Pre-owned Car Loan
-
Two Wheeler Loan
-
Pre-owned Two
Wheeler Loan -
Commercial Vehicle
Loan -
Gold Loan
-
Loan Against Property
-
Loan Against Securities
-
Easy Buy EMI card
-
Personal Loan
EMI Calculator -
Education Loan
EMI Calculator -
Home Loan
EMI Calculator
- IDFC FIRST Bank Wealth & Insure
-
FIRST Select
-
FIRST Wealth
-
FIRST Private
-
Mutual Funds
-
Sovereign Gold Bond
-
Demat Account
-
Term Insurance
-
Life Insurance
-
Health Insurance
-
General Insurance
-
Bonds
-
Loan Against
Securities -
Portfolio Management
Service
- IDFC FIRST Bank Payments
-
FASTag
-
Credit Card
Bill Payments -
UPI
-
Funds Transfer
-
Forex Services
-
Pay Loan EMI
- IDFC FIRST Bank Cards
-
Ashva :
Metal Credit Card -
Mayura :
Metal Credit Card -
FIRST Millennia
Credit Card -
FIRST Classic
Credit Card -
FIRST Select
Credit Card -
FIRST Wealth
Credit Card -
FIRST WOW!
Credit Card -
Deals
-
Debit Cards
-
Co-branded Cards
-
Credit Card
EMI Calculator -
FIRST Corporate
Credit Card -
FIRST Purchase
Credit Card -
FIRST Business
Credit Card
- Premium Metal Credit Cards
-
AshvaLifestyle1% Forex₹2,999
-
MayuraLifestyleZero Forex₹5,999
-
FIRST PrivateInvite Only
- Best for travellers
-
MayuraZero ForexMetal₹5,999
-
Ashva1% ForexMetal₹2,999
-
FIRST WOW!Zero ForexTravelLifetime Free
-
FIRST SWYPTravel OffersEMI₹499
-
FIRST Select1.99% ForexLifestyleLifetime Free
-
FIRST Wealth1.5% ForexLifestyleLifetime Free
-
Club VistaraTravelLifestyle₹4,999
-
IndiGo IDFC FIRST Dual Credit CardTravelLifestyle₹4,999
- Max benefits, Free for life
-
FIRST Classic10X RewardsShoppingNever Expiring Rewards
-
FIRST Millennia10X RewardsShoppingNever Expiring Rewards
-
FIRST Select10X RewardsLifestyle1.99% Forex
-
FIRST Wealth10X RewardsLifestyle1.5% Forex
-
FIRST WOW!RewardsTravelZero Forex
-
LIC ClassicRewardsInsuranceShopping
-
LIC SelectRewardsInsuranceShopping
- Reward Multipliers
-
AshvaLifestyleMetal₹2,999
-
MayuraLifestyleZero Forex₹5,999
-
FIRST ClassicNever Expiring RewardsShoppingLifetime Free
-
FIRST MillenniaNever Expiring RewardsShoppingLifetime Free
-
FIRST SelectNever Expiring RewardsLifestyleLifetime Free
-
FIRST WealthNever Expiring RewardsLifestyleLifetime Free
- Rewards & Credit on UPI
-
FIRST Power+FuelUPI₹499
-
FIRST PowerFuelUPI₹199
-
FIRST EA₹NVirtual1% Cashback₹499
-
FIRST DigitalVirtualUPI₹199
-
IndiGo IDFC FIRST Dual Credit CardUPITravelDual cards
- Fuel and Savings
-
FIRST PowerRewardsUPI₹199
-
FIRST Power+RewardsUPI₹499
-
LIC ClassicRewardsInsuranceShopping
-
LIC SelectRewardsInsuranceShopping
- Express and Flaunt
-
AshvaMetal1% Forex₹2,999
-
MayuraMetalZero Forex₹5,999
-
FIRST SWYPEMIOfferMAX₹499
-
FIRST MillenniaRewardsShoppingLifetime Free
- FD Backed rewarding Credit Cards for all
-
FIRST EA₹NVirtualCashback₹499
-
FIRST WOW!Zero ForexTravelLifetime Free
-
CreditPro Balance TransferTransfer & SaveReduce InterestPay Smartly
- IDFC FIRST Bank NRI Forex Solutions
-
Send money to India-Wire transfer
-
Send money to India-Digitally
-
Send money abroad
-
Max Returns FD (INR)
- IDFC FIRST Bank MSME Accounts
-
Platinum Current
Account -
Gold
Current Account -
Silver Plus
Current Account -
Merchant Multiplier
Account -
Agri Multiplier
Account -
TASC Institutional
Account -
Dynamic Current
Account -
World business
Account -
First Startup
Current Account
- IDFC FIRST Bank Business Loans
-
Business Loan
-
Professional Loan
-
Loan Against Property
-
Business Loan for Women
-
Working Capital Loan
-
Construction Equipment Loan
-
Machinery Loan
-
Healthcare Equipment Loan
- IDFC FIRST Bank Business Solutions
-
Payment Solutions
-
Tax Payments
-
Doorstep Banking
-
Point of Sale (POS)
-
Escrow Accounts
-
NACH
-
Payment Gateway
-
UPI
-
Virtual Accounts
-
As per amendment in the Income Tax Rules, PAN or Aadhaar are to be mandatorily quoted for cash deposit or withdrawal aggregating to Rupees twenty lakhs or more in a FY. Please update your PAN or Aadhaar. Kindly reach out to the Bank’s contact center on 1800 10 888 or visit the nearest IDFC FIRST Bank branch for further queries.
-
-
Most Searched
Sorry!
We couldn’t find ‘’ in our website
Here is what you can do :
- Try checking the spelling and search
- Search from below suggestions instead
- Widen your search & try a more generic keyword
Suggested
Get a Credit Card
Enjoy Zero Charges on All Commonly Used Savings Account Services
Open Account Now
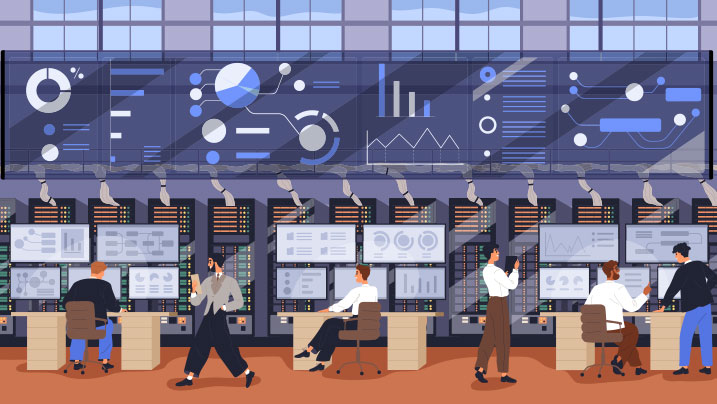
Buoyed by digital transformation initiatives, businesses have doubled down on digitization and online services. But this rapid progress and digitization come at a price. Cyber threats to the financial services industry are growing in frequency and scope, aimed at exploiting weaknesses, disrupting systems, stealing data and funds. The frequency and sophistication of these attacks continue to rise since criminals use every loophole they can for malicious purposes.
Who can forget Equifax? The credit-monitoring company suffered a severe setback when a breach exposed the private data of more than 160 million users. While Equifax spent hundreds of millions in settlements and damage control (the damages piled up to a whopping $700 million), Wall Street lowered the company’s valuation by $4 billion.
READ MORE
With the growth in cybercrime and security breach incidents, cybersecurity spend has risen exponentially in the past decade with no signs of abating. Gartner estimates that spending on information security and risk management will total $172 billion in 2022. Despite this staggering investment, the stakes keep getting higher. Business leaders today understand that the true cost of a breach goes far beyond the financial implications of an attack, often resulting in lawsuits, reputational loss, logistical headaches, and angry customers. To avoid these circumstances, cybersecurity teams are now assessing the role of technology such as blockchain to offer stronger transactional security and risk management measures.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed network with millions of users across the world. Each user has access to the blockchain and all the data in the blockchain is secured with cryptography. All other members are responsible for verifying that the data added to the blockchain is accurate. In a nutshell, it is a digital, distributed, and decentralized public ledger that enables the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network.
Why is Blockchain security promising for cybersecurity and risk management?
The cybersecurity industry benefits from blockchain’s unique features that create a practically impenetrable wall between the hacker and the system. The inherently decentralized, cryptographic principles and consensuses-based nature of blockchain makes it impossible for data to be tampered with. It also provides high standards of data transparency and integrity.
The three main tenets of blockchain security are:
1. Decentralization
Blockchain is not owned by any single individual.
2. Transparency with pseudonymity
All blockchain transactions and corresponding values are visible to anyone who has access to the system. Each node or user on a blockchain has a unique alphanumeric address identifier. Transactions take place between blockchain addresses allowing complete transparency while protecting privacy.
3. Immutability
Once a transaction is added to the database, the records cannot be tampered with because they are linked to every previous transaction record.
When analyzed in the context of cybersecurity, these three laws make blockchain a potential solution for building secure and impenetrable systems. The most important argument for using blockchain in cybersecurity is that it eliminates the risk of a single point of failure.
Blockchain use cases for cybersecurity
Blockchain’s promise as one of the most secure ways to carry out transactions in the digital world has made it an attractive proposition for many sectors, including financial services. Leveraging its integrity assurance, organizations can build cybersecurity solutions for many other applications and technologies. Here are some use cases of blockchain to boost cybersecurity:
1. End user security
Hackers are increasingly using edge devices like thermostats and routers to break into systems. With the rapid adoption of smart devices and home automation, it is quite easy for a cybercriminal to gain access through central administration or edge devices.
Blockchain can help secure IoT systems and end user devices by decentralizing their administration. This means the device can make security decisions on its own without relying on a central admin or authority. These advantages are among the main reasons the technology is being widely used in financial institutions, such as banks. For example, end-user security is a particularly difficult issue in banks. Simple logins, centralized IT infrastructure and weak passwords frequently allow cyber attackers to enter network infrastructure. The usage of blockchains enables users and devices to be authenticated without passwords through multi-party verification via blockchain-based SSL certificates. The distributed and decentralized nature of the network that checks the integrity of transactions and account balances makes attacks virtually impossible.
2. DNS and DDoS attack mitigation
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) is when cybercriminals flood a network with so much malicious traffic that it cannot operate normally. These attacks slow down or shut down the website or resource systems completely. In case of Domain Name System (DNS) attacks, a bad actor will either compromise a network’s DNS or take advantage of its underlying attributes to carry out a wider attack.
Blockchain technology could enable the establishment of peer-to-peer (P2P) and zero-trust networks, removing the requirement for devices to trust one another and eliminating the necessity for a centralized, single point of failure. Organizations can make a node under assault redundant and continue to operate as usual. As a result, even if a large portion of the blockchain network is attacked, the system will continue to function due to its distributed structure.
3. KYC verification
Fraudulent e-KYC update is one of the most recent ways that scammers are deceiving naïve individuals. Posing as a service provider, fraudsters ask for sensitive information such as Aadhaar numbers and bank account details. This is a scenario that a blockchain-based KYC verification method can help avoid.
Blockchain technology, as a decentralized ledger, would enable the collection and storage of data from various governments and private data portals into a single unchangeable, safe database. Cryptographic keys — a means for encoding data in machine-readable form – are used to protect each user's personal information on the ledger. Hackers and cybercriminals will have a difficult time breaking the keys and gaining access to necessary credentials.
What the future holds
Given blockchain's various applications, such as facilitating transactions and storing data in a more secure manner, the financial services industry stands to benefit greatly from its growth. Emerging technologies such as permissioned blockchains can help achieve the important goals of combating cybersecurity risk and adequately protecting consumers' financial information and the integrity of the global financial system as cyber threats to the industry continue to evolve in complexity and intensity.
Disclaimer
The contents of this article/infographic/picture/video are meant solely for information purposes. The contents are generic in nature and for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for specific advice in your own circumstances. The information is subject to updation, completion, revision, verification and amendment and the same may change materially. The information is not intended for distribution or use by any person in any jurisdiction where such distribution or use would be contrary to law or regulation or would subject IDFC FIRST Bank or its affiliates to any licensing or registration requirements. IDFC FIRST Bank shall not be responsible for any direct/indirect loss or liability incurred by the reader for taking any financial decisions based on the contents and information mentioned. Please consult your financial advisor before making any financial decision.
The features, benefits and offers mentioned in the article are applicable as on the day of publication of this blog and is subject to change without notice. The contents herein are also subject to other product specific terms and conditions and any third party terms and conditions, as applicable. Please refer our website www.idfcfirstbank.com for latest updates.